1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
|
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
##
#
# Modèle ISA
# Valeurs de référence au niveau de la mer
# MSL = Mean Sea Level
##
MSL_PRESSURE = 101325 # Pression (pa)
MSL_TEMPERATURE_CELSIUS = 15 # Température (°C)
MSL_TEMPERATURE_KELVIN = 288.15 # Température (K)
MSL_rho = 1.225 # kg/m3
# Calcul du nombre de mach
# Vc = Vitesse Conventionnelle
COEFF_COMPRESSIBILITE_AIR = 1.4
CSTE_SPECIFIQUE_AIR = 287
CSTE_KNOT = 1.852 # 1 noeud = 1.852 km/h
CSTE_FEET = 0.3048 # 1 pied = 0,3048 m
CSTE_ms_kmh = 3.6 # 1 m/s = 3.6 km/h
def convertMetertoFeet(meter):
return meter / CSTE_FEET
def convertFeettoMeter(feet):
return feet * CSTE_FEET
#
#
#
def convertSpeedMsToKmh (speed_ms):
return speed_ms * CSTE_ms_kmh
def convertSpeedKmhToMs (speed_kmh):
return speed_kmh / CSTE_ms_kmh
def convertSpeedKnotToKmh (speed_knot):
return speed_knot * CSTE_KNOT
def convertSpeedKmhToKnot (speed_kmh):
return speed_kmh / CSTE_KNOT
#
#
#
def computeStaticPressure(altitude_m):
return MSL_PRESSURE * (1-(0.0065 * altitude_m)/MSL_TEMPERATURE_KELVIN)**5.255
def computeTotalPressure(staticPressure_Pa, machNumber):
return staticPressure_Pa * (1 + (COEFF_COMPRESSIBILITE_AIR-1) /2 * machNumber**2)**(COEFF_COMPRESSIBILITE_AIR/(COEFF_COMPRESSIBILITE_AIR-1))
def computeCalibratedAirSpeed(staticPressure_Pa, totalPressure_Pa):
exposant = (COEFF_COMPRESSIBILITE_AIR- 1)/COEFF_COMPRESSIBILITE_AIR
membre_1 = (totalPressure_Pa - staticPressure_Pa)/MSL_PRESSURE
membre_2 = 2/exposant
membre_3 = MSL_PRESSURE / MSL_rho
return np.sqrt((((membre_1 + 1)**exposant - 1)) * membre_2 * membre_3)
def computeMachNumber (staticPressure_Pa, Vc_ms):
step_01 = (COEFF_COMPRESSIBILITE_AIR-1)/(2*COEFF_COMPRESSIBILITE_AIR)
step_02 = step_01 * (MSL_rho/MSL_PRESSURE) * (Vc_ms **2)
step_03 = (1 + step_02)**((COEFF_COMPRESSIBILITE_AIR)/(COEFF_COMPRESSIBILITE_AIR - 1)) - 1
step_04 = (MSL_PRESSURE/staticPressure_Pa) * step_03
step_05 = (step_04 + 1)**((COEFF_COMPRESSIBILITE_AIR-1)/COEFF_COMPRESSIBILITE_AIR)
step_06 = 2/(COEFF_COMPRESSIBILITE_AIR-1) * (step_05 - 1)
return np.sqrt(step_06)
#conditions initiales des calculs
Zp_Vector_ft = np.arange (0, 36500, 500) # Variation d'altitude par tranche de 500ft
Mach_Vector = np.arange(0, 1, 0.1) # Subsonique : variation par 0,1 point de mach
Vc_Vector_knot = np.arange (0, 560, 50) # Variation de vitesse par tranche de 10 noeuds
# Calcul de Ps(Zp)
staticPressure_Vector_Pa = computeStaticPressure(convertFeettoMeter(Zp_Vector_ft))
# Calcul de Pt(Ps, M)
totalPressure_Vector_Pa = computeTotalPressure(staticPressure_Vector_Pa[:, None], Mach_Vector)
#Calcul de Vc(Ps, Pt)
# staticPressure_Vector_Pa = staticPressure_Vector_Pa[:, None] * np.ones(10)
Vc_array = computeCalibratedAirSpeed(staticPressure_Vector_Pa[:, None] * np.ones(10), totalPressure_Vector_Pa)
Vc_array = convertSpeedMsToKmh(Vc_array)
Vc_array = convertSpeedKmhToKnot(Vc_array)
Vc_array = np.around(Vc_array)
#Calcul du Mach(Ps, Vc)
Mach_array = computeMachNumber(staticPressure_Vector_Pa[:, None] * np.ones(12), convertSpeedKnotToKmh(convertSpeedKmhToMs(Vc_Vector_knot)))
Mach_array = np.around(Mach_array, 2)
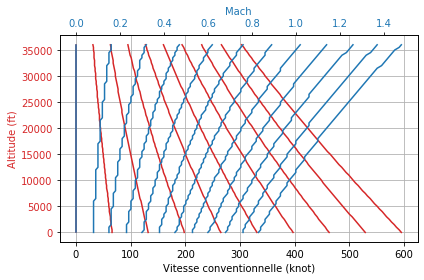
plt.title("Abaque Chevalier")
plt.xlabel("Vitesse conventionnelle (knot)")
plt.ylabel("Altitude (ft)")
plt.grid(True)
fig, ax1 = plt.subplots()
color = 'tab:red'
ax1.set_xlabel('Vitesse conventionnelle (knot)')
ax1.set_ylabel('Altitude (ft)', color=color)
ax1.plot(Vc_array, Zp_Vector_ft, color=color)
ax1.grid(True)
ax1.tick_params(axis='y', labelcolor=color)
ax2 = ax1.twiny() # instantiate a second axes that shares the same x-axis
color = 'tab:blue'
ax2.set_xlabel('Mach', color=color) # we already handled the x-label with ax1
ax2.plot(Mach_array, Zp_Vector_ft, color=color)
ax2.tick_params(axis='x', labelcolor=color)
fig.tight_layout() # otherwise the right y-label is slightly clipped
plt.show() |











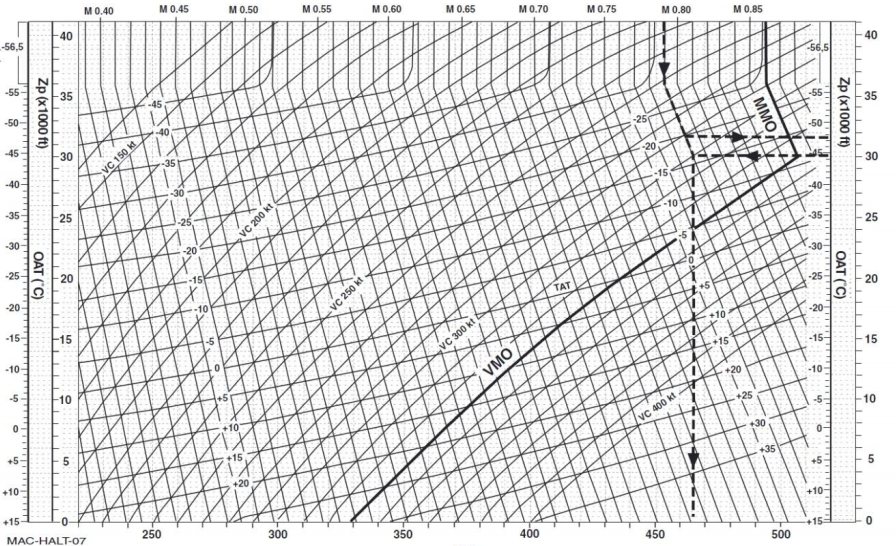
 Répondre avec citation
Répondre avec citation
Partager